In DevOps, Python offers various data types and data structures that are commonly used for efficient data handling and manipulation.
Data Types
Data types are the classification or categorization of data items. It represents the kind of value that tells what operations can be performed on a particular data.
Since everything is an object in Python programming, data types are actually classes and variables are instance (object) of these classes.
python is a dynamically typed language; hence we do not need to define the type of the variable while declaring it. The interpreter implicitly binds the value with its type.
Python has the following data types built-in by default, in these categories:
Text Type: |
|
Numeric Types: |
|
Sequence Types: |
|
Mapping Type: |
|
Set Types: |
|
Boolean Type: |
|
Binary Types: |
|
None Type: |
|
Data Structures
Data Structures are a way of organizing data so that it can be accessed more efficiently depending upon the situation. Data Structures are fundamentals of any programming language around which a program is built. Python helps to learn the fundamental of these data structures in a simpler way as compared to other programming languages.
Types of Data Structures in Python
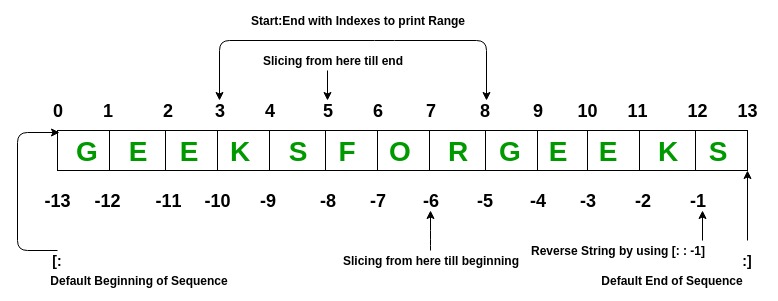
List:
List elements can be accessed by the assigned index. In python starting index of the list, sequence is 0 and the ending index is (if N elements are there) N-1.

Tuple: Python Tuple is a collection of Python objects much like a list but Tuples are immutable i.e. the elements in the tuple cannot be added or removed once created. Just like a List, a Tuple can also contain elements of various types.

Dictionary: Python dictionary is like hash tables in any other language with the time complexity of O(1). It is an unordered collection of data values, used to store data values like a map, which, unlike other Data Types that hold only a single value as an element, Dictionary holds the key:value pair. Key-value is provided in the dictionary to make it more optimized

Tasks:
Give the Difference between List, Tuple and set.
ist
Tuple
Set
Dictionary
List can be represented by [ ]
Tuple can be represented by ()
Set can be represented by { }
Dictionary can be represented by { }
List allows duplicate elements
Tuple allows duplicate elements
Set will not allow duplicate elements
Dictionary doesn’t allow duplicate keys.
List can use nested among all
Tuple can use nested among all
Set can use nested among all
Dictionary can use nested among all
Example: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Example: (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
Example: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Example: {1: “a”, 2: “b”, 3: “c”, 4: “d”, 5: “e”}
List is ordered
Tuple is ordered
Set is unordered
Dictionary is ordered (Python 3.7 and above)
Create the below Dictionary and use Dictionary methods to print your favorite tool just by using the keys of the Dictionary.
fav_tools =
{ 1:"Linux",
2:"Git",
3:"Docker",
4:"Kubernetes",
5:"Terraform",
6:"Ansible",
7:"Chef"
}

Create a List of cloud service providers eg.
cloud_providers = ["AWS","GCP","Azure"]

These data types and structures in Python provide a rich set of tools for handling and manipulating data in DevOps workflows. Understanding their characteristics and functionalities allows you to choose the most appropriate ones for your specific requirements.
Thanks for reading my article. Have a nice day.
For updates follow me on LinkedIn: Suraj Barik
Hashtags:
#90daysofdevops #devops #cloud #aws #awscloud #awscommunity #docker #linux #github #opensource #challenge #learningprogress #linkedin #trainwithshubham #devopscommunity #cloudproviders #bash #bashshellscripting
